IBM Watson blends existing and innovative technology into a new approach called cognitive computing. At the simplest operational level it is technology for asking natural language-based questions, getting answers and support appropriate action to be taken or provide information to make more informed decisions.
IBM Watson blends existing and innovative technology into a new approach called cognitive computing. At the simplest operational level it is technology for asking natural language-based questions, getting answers and support appropriate action to be taken or provide information to make more informed decisions. The  technology relies on massive processing power to yield probabilistic responses to user questions using sophisticated analytical algorithms. A cognitive system like Watson accesses structured and unstructured information within an associated knowledge base to return responses that are not simply data but contextualized information that can inform users’ actions and guide their decisions. This is a gigantic leap beyond human decision-making using experience based on random sources from the industry and internal sets of reports and data.
technology relies on massive processing power to yield probabilistic responses to user questions using sophisticated analytical algorithms. A cognitive system like Watson accesses structured and unstructured information within an associated knowledge base to return responses that are not simply data but contextualized information that can inform users’ actions and guide their decisions. This is a gigantic leap beyond human decision-making using experience based on random sources from the industry and internal sets of reports and data.
This innovative new approach to computing is designed to aid humans by working with natural language – English in the case of today’s Watson. This approach earned Watson the 2012 Technology Innovation Award in the category of Overall Operational Innovation.
For those of you who are not used to the word cognitive, the foundation of cognition is the sum of all the thinking processes that contribute to gaining knowledge for problem-solving. In computational systems these processes are modeled using hardware and software; machine-based cognition thus is a step toward imbuing an artificial system with attributes we typically consider human: the abilities to think and learn. Watson builds on a foundation of evidence from preexisting decisions and knowledge sources that it can load for reference in future inquiries. The evidence-based reasoning that Watson employs to answer question is part of the big deal in its approach.
Watson supports three types of engagement – ask, discover and decide – that take natural language questions, find facts to support a decision process, then gets probabilistic guidance on decisions. This goes beyond search and retrieval technology; machine learning and processing of questions using very large volumes of data, commonly referred to as big data, is the foundation on which Watson as a cognitive system operates. Most important is the continuous learning method and what I would call adaptive intelligence. While machine learning and pattern-based analytics are part of the cognitive system, the ability to process big data efficiently to provide a probabilistic set of recommendations is just the kind of innovation many industries need.
IBM has focused much of its work on Watson on healthcare, with potential life-saving implications in an environment where doctors must make crucial decisions in the midst of pressure from the complexity, costs, overload of information and policies. Watson can ingest large volumes of information from reports and documents that can accelerate its learning processes to support a range of healthcare needs. Watson can be used in three areas in healthcare: teaching, practice and payment. IBM works with Wellpoint to support doctors in making decisions, and also eliminating waste or misapplied treatments that insurance providers have to cover. Watson is being used today to determine where improvements can be made in cancer treatment. IBM has targeted specific Watson solutions to help in the research, diagnosis and treatment, care and utilization aspects of battling cancer.
IBM has a huge opportunity to bring innovation to business 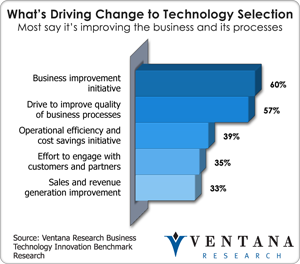 through the use of Watson, and has been experimenting with a number of deployments to test its potential. Innovative technology is a priority today for business improvement initiatives (60%) and to improve the quality of business processes (57%) – the top two factors driving technology selection according to our business technology innovation benchmark research. IBM has been working with organizations in healthcare and financial services, but believes Watson could be useful in just about every industry that must have what I call better situation intelligence that must accommodate current conditions and preexisting information to determine the best answer. While IBM will not be the only supplier of cognitive systems, it is pretty much the sole supplier of one that can be purchased and adapted to a business today. IBM is still working to improve the methods by which its cognitive system operates, as well as the interface with which it delivers answers. As IBM moves forward, it will be challenged to create attractive packages and prices for Watson and its computing technology (i.e. hardware, memory, storage and processing potential), as this new approach is not something that organizations have experienced before. Despite this challenge, IBM Watson represents a step forward that the IT and technology industry does not see very often. After my assessment of IBM Watson at the IBM Analyst Insights (Twitter: @AnalystInsights) where I got to have an in depth discussion with the leaders of IBM Watson provided more insight to what is possible with the technology and path for its investments into its cognitive system. I would recommend that organizations take a look at the future of business technology computing that will be able to make a significant impact on the operations of any organization.
through the use of Watson, and has been experimenting with a number of deployments to test its potential. Innovative technology is a priority today for business improvement initiatives (60%) and to improve the quality of business processes (57%) – the top two factors driving technology selection according to our business technology innovation benchmark research. IBM has been working with organizations in healthcare and financial services, but believes Watson could be useful in just about every industry that must have what I call better situation intelligence that must accommodate current conditions and preexisting information to determine the best answer. While IBM will not be the only supplier of cognitive systems, it is pretty much the sole supplier of one that can be purchased and adapted to a business today. IBM is still working to improve the methods by which its cognitive system operates, as well as the interface with which it delivers answers. As IBM moves forward, it will be challenged to create attractive packages and prices for Watson and its computing technology (i.e. hardware, memory, storage and processing potential), as this new approach is not something that organizations have experienced before. Despite this challenge, IBM Watson represents a step forward that the IT and technology industry does not see very often. After my assessment of IBM Watson at the IBM Analyst Insights (Twitter: @AnalystInsights) where I got to have an in depth discussion with the leaders of IBM Watson provided more insight to what is possible with the technology and path for its investments into its cognitive system. I would recommend that organizations take a look at the future of business technology computing that will be able to make a significant impact on the operations of any organization.
Regards,
Mark Smith
CEO & Chief Research Officer







