Hackers have turned to exploiting website optimization platform Google Analytics to steal credit cards, passwords, IP addresses and a whole host of compromising information that can be shared by hacked sites.
According to an investigation from Kaspersky Lab, a new hacking technique that?s been developed to tap into Google Analytics to steal confidential data surrounding payment cards and passwords among much more information that can be exploited.
However, Search Engine Journal reports that the issue isn?t directly the fault of any frailty within Google Analytics itself, rather it exploits the trusted status given to the analytics engine by all browsers in order to steal information from hacked sites by utilizing Google Analytics as a middleman for transferring that data.
The research report released by Kaspersky Lab stated that the cybersecurity watchdog ?identified several cases where the service was misused: attackers injected malicious code into sites, which collected all the data entered by users, and then sent it via Analytics. As a result, the attackers could access the stolen data in their Google Analytics account.?
The report also pointed out that the exploit steals everything that?s shared with the compromised website. Whilst it includes credit card information, it presumably will also mean password details, too.
?The script collects everything anyone inputs on the site (as well as information about the user who entered the data: IP address, User Agent, time zone). The collected data is encrypted and sent using the Google Analytics Measurement Protocol,? the Kaspersky report notes.
Stealing Credit Cards With Google Analytics
It?s worth noting that for a site to be exploited by Google Analytics, it first has to be operating on an inadvertently exploitable framework – owing to vulnerable software that doesn?t put up much of a fight against attackers.
Once it?s been compromised, the hacker will upload code that siphons sensitive information that visitors will share on the site?s pages, such as passwords and payment card numbers.
Google Analytics software is free to use and helps website owners and marketers alike to measure the traffic arriving from other sites and external sources to their own. The platform is primarily designed to help businesses and site owners to understand how visitors are interacting with their pages.
Although it?s often used as a way of tracking marketing and ad campaigns by monitoring where traffic is arriving from, the tool has drawn the attention of criminals – with attackers stealing user information by adding their own Google Analytics codes into a website, exploiting the platform by getting it to send the code to them.
Exploiting Header Flaws
Security headers are known for being an effective way of securing a website against attacks such as cross-site scripting and script injection as a means of preventing data theft attacks.
One of the more notable security headers is known as a Content Security Policy (CSP) header. CSP headers can tell browsers which domains are trusted for downloading scripts. This acts as a sort of failsafe to prevent hackers from downloading viruses from other websites onto a site visitor?s browser.
However, according to Hacker News, a flaw within CSP headers is that on sites using Google Analytics, the platform is specified in the CSP as a trustworthy source of scripts. Due to this, hackers can add their own Google Analytics codes on to websites and bypass content security protocols – Google?s Content Security Policy powerless to resist.
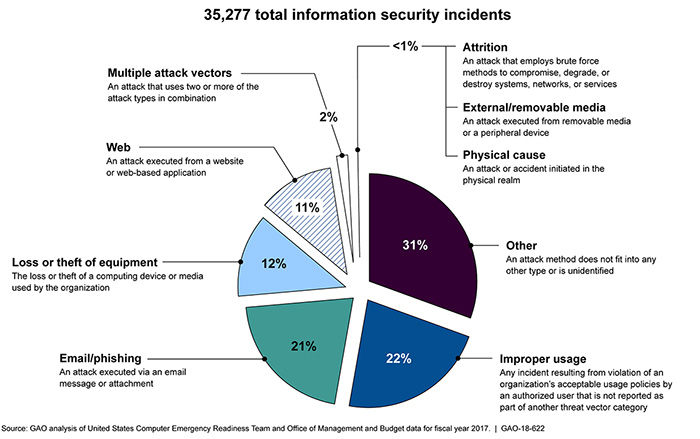
As we can see, web-based attacks amount for around 11% of online security incidents, illustrating the effectiveness of preventative measures embedded into websites. The arrival of a flaw within arguably the world?s most advanced free-to-use website analytics engine is a huge concern for Google and eCommerce business owners alike.
How to Ensure That Your Business is Protected Against The Exploit
One of the more effective ways to know whether your website has been affected by the exploit is to check whether there?s more than one Google Analytics code on your site.
If a different Google Analytics code has completely replaced your own code, then this would be noticeable by the fact that the platform will be reporting zero traffic on your account.
However, the act of removing a fraudulent analytics code may not be enough to salvage your site from exploits. If another code exists then it might mean that an underlying vulnerability on the site has allowed a hacker to embed the fraudulent code in the first place.
Google Analytics has quickly evolved into one of the most powerful and cost-effective website analysis tools online. This is largely unsurprising, given how dominant Google?s search engine is online. With the vast majority of online traffic arriving at websites from Google searches, the internet behemoths have become powerful enough to set their own rules on web performance.
However, the emergence of vulnerabilities in Google Analytics will be unnerving news to businesses who rely on online sales to win customers. There is a whole host of alternative solutions on hand for companies happy to pay a premium in order to retain a deep level of metrics alongside security, and Countly is one example of a platform that promises ?secure web analytics?.
Although you have to request a demo to get started. If you need an enterprise edition, it may come at a dollar.
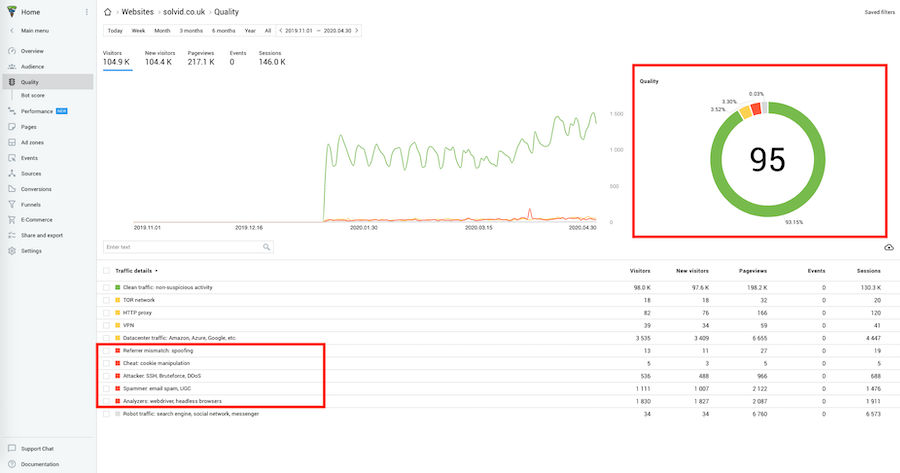
Another good alternative to Google Analytics is Finteza. In fact, the tool has one extra powerful feature that is lacking in Google Analytics – traffic quality analysis.
The feature automatically identifies the quality of incoming traffic and assigns it under a specific category (e.g. ?Clean Traffic?, ?Bot traffic?, ?Cookie Manipulation?, ?Spam?, and more).
The Necessity of Security
The devastation caused by cyber attacks is increasing at an alarming rate. Not only should we be concerned about the volume of web-based hacking but also the rise in financial damage that modern cyber-attacks are causing.
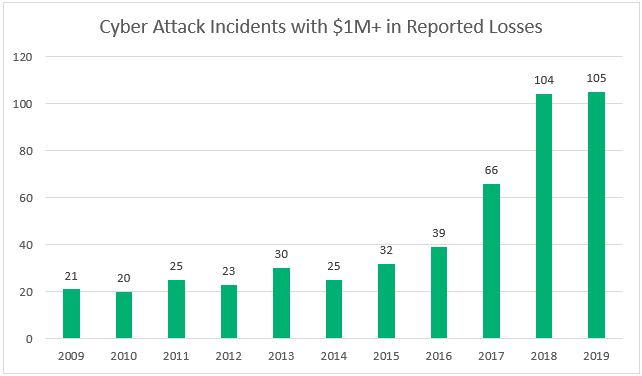
According to Infosec statistics, cyber-attacks resulting in over $1 million in reported losses has risen exponentially over the past five years – with over 100 cases reported in both of 2018 and 2019.
As businesses come to terms with the inevitability of global recessions and a widespread loss of consumer spending power, 2020 has served as a reminder to businesses to shore up their defences against unwelcome visitors. With this in mind, let?s explore some key tips for keeping your eCommerce business and customers safe from mounting threats online:
1. Befriend Your Filters
It can be extremely useful to set up email and browser filters in order to repel cyber hackers and stop spam from entering employee inboxes. It?s also possible to download blacklist services to block anybody on your server from navigating onto ?risky? websites that could pose malware risks.
Be sure to caution employees about visiting hazardous websites while on the company?s server. While you would expect workers to avoid explicit websites at work, the risks associated with one employee falling into the trap of downloading malware are too sizeable to turn a blind eye to.
2. Always Ensure Sensitive Information is Encrypted
Utilise full-disk encryption in order to keep your company?s computers, tablets and smartphones protected at all times. Save your encryption password or key in a secure location that?s far removed from your stored backups too.
Email recipients tend to require the same encryption capability in order to decrypt, so it?s important to never send the password or key in the same email as an encrypted document. Providing it via different means like by phone is a strong way of remaining secure.
3. Dispose of Your Old Equipment Safely
Successful offices are always at the forefront of innovation, which means that it?s usual to see computers come and go as workplaces look to upgrade on their in-house technology.
However, before donating, selling on, or throwing away your old computers, it?s vital that you wipe all the valuable information from their hard drives. Delete all sensitive business and personal data on old CDs, flash drives and other forms of media before taking them to a company that can securely dispose of them on your behalf.
The same practice should, of course, go for sensitive paper information. Aim to dispose of paper documents with a crosscut shredder or incinerator.
4. Secure Your Networks
It?s important to never rest on your laurels when it comes to securing your network. Always look to change the passwords on new routers, rather than opting for the supplied admin keys, and make sure your wireless access points don?t broadcast its service set identifier (SSID).
Set your router to use WiFi Protected Access 2 (WPA-2) and ensure that you use Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for your encryption. Ensuring that your networks are secure should be seen as one of the most vital challenges your business faces when moving into a new office or setting up with a new internet provider. It?s also important to avoid using Wired-Equivalent Privacy (WEP) to uphold a greater level of security.
Additionally, if you provide wireless internet access to customers or visitors, be sure to make it separate from the network that your business uses.
As some users of Google Analytics may have found out recently, even the largest brands on the internet are vulnerable to frailties in providing security to their users. At a time when companies across the world are beginning to feel the pinch from looming recessions, it?s more vital than ever to ensure that your services are strong enough to keep your customers and cash flow protected at all times.










